Big O notation is a powerful tool used in computer science to describe the time complexity or space complexity of algorithms. It provides a standardized way to compare the efficiency of different algorithms in terms of their worst-case performance. Understanding Big O notation is essential for analyzing and designing efficient algorithms.
In this tutorial, we will cover the basics of Big O notation, its significance, and how to analyze the complexity of algorithms using Big O.
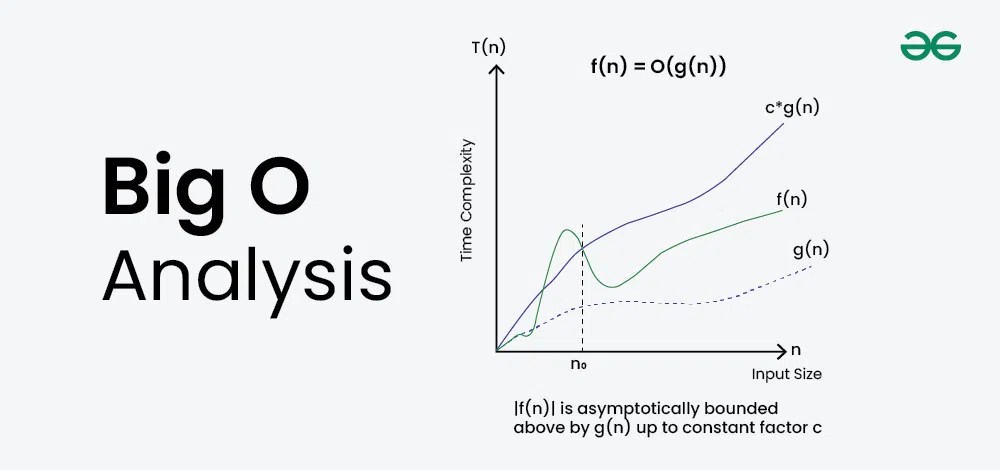
Table of Content
- What is Big-O Notation?
- Definition of Big-O Notation:
- Why is Big O Notation Important?
- Properties of Big O Notation
- Common Big-O Notations
- How to Determine Big O Notation?
- Mathematical Examples of Runtime Analysis
- Algorithmic Examples of Runtime Analysis
- Algorithm Classes with Number of Operations and Execution Time
- Comparison of Big O Notation, Big Ω (Omega) Notation, and Big θ (Theta) Notation
- Frequently Asked Questions about Big O Notation
What is Big-O Notation?
Big-O, commonly referred to as “Order of”, is a way to express the upper bound of an algorithm’s time complexity, since it analyses the worst-case situation of algorithm. It provides an upper limit on the time taken by an algorithm in terms of the size of the input. It’s denoted as O(f(n)), where f(n) is a function that represents the number of operations (steps) that an algorithm performs to solve a problem of size n.
Big-O notation is used to describe the performance or complexity of an algorithm. Specifically, it describes the worst-case scenario in terms of time or space complexity.
Important Point:
- Big O notation only describes the asymptotic behavior of a function, not its exact value.
- The Big O notation can be used to compare the efficiency of different algorithms or data structures.
Definition of Big-O Notation:
Given two functionsf(n)andg(n), we say thatf(n)isO(g(n))if there exist constantsc > 0andn0 >= 0such thatf(n) <= c*g(n)for alln >= n0.
In simpler terms,f(n)isO(g(n))iff(n)grows no faster thanc*g(n)for all n >= n0 where c and n0 are constants.
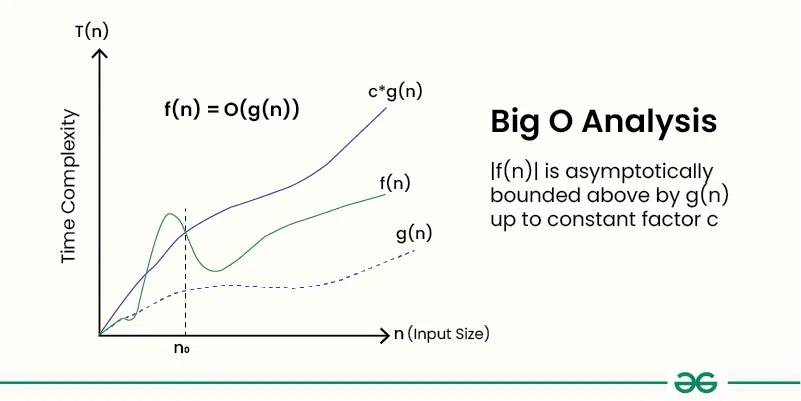
Why is Big O Notation Important?
Big O notation is a mathematical notation used to describe the worst-case time complexity or efficiency of an algorithm or the worst-case space complexity of a data structure. It provides a way to compare the performance of different algorithms and data structures, and to predict how they will behave as the input size increases.
Big O notation is important for several reasons:
- Big O Notation is important because it helps analyze the efficiency of algorithms.
- It provides a way to describe how the runtime or space requirements of an algorithm grow as the input size increases.
- Allows programmers to compare different algorithms and choose the most efficient one for a specific problem.
- Helps in understanding the scalability of algorithms and predicting how they will perform as the input size grows.
- Enables developers to optimize code and improve overall performance.
Properties of Big O Notation:
Below are some important Properties of Big O Notation:
1. Reflexivity:
For any function f(n), f(n) = O(f(n)).
Example:
f(n) = n2, then f(n) = O(n2).
2. Transitivity:
If f(n) = O(g(n)) and g(n) = O(h(n)), then f(n) = O(h(n)).
Example:
f(n) = n3, g(n) = n2, h(n) = n4. Then f(n) = O(g(n)) and g(n) = O(h(n)). Therefore, f(n) = O(h(n)).
3. Constant Factor:
For any constant c > 0 and functions f(n) and g(n), if f(n) = O(g(n)), then cf(n) = O(g(n)).
Example:
f(n) = n, g(n) = n2. Then f(n) = O(g(n)). Therefore, 2f(n) = O(g(n)).
4. Sum Rule:
If f(n) = O(g(n)) and h(n) = O(g(n)), then f(n) + h(n) = O(g(n)).
Example:
f(n) = n2, g(n) = n3, h(n) = n4. Then f(n) = O(g(n)) and h(n) = O(g(n)). Therefore, f(n) + h(n) = O(g(n)).
5. Product Rule:
If f(n) = O(g(n)) and h(n) = O(k(n)), then f(n) * h(n) = O(g(n) * k(n)).
Example:
f(n) = n, g(n) = n2, h(n) = n3, k(n) = n4. Then f(n) = O(g(n)) and h(n) = O(k(n)). Therefore, f(n) * h(n) = O(g(n) * k(n)) = O(n5).
6. Composition Rule:
If f(n) = O(g(n)) and g(n) = O(h(n)), then f(g(n)) = O(h(n)).
Example:
f(n) = n2, g(n) = n, h(n) = n3. Then f(n) = O(g(n)) and g(n) = O(h(n)). Therefore, f(g(n)) = O(h(n)) = O(n3).
Common Big-O Notations:
Big-O notation is a way to measure the time and space complexity of an algorithm. It describes the upper bound of the complexity in the worst-case scenario. Let’s look into the different types of time complexities:
1. Linear Time Complexity: Big O(n) Complexity
Linear time complexity means that the running time of an algorithm grows linearly with the size of the input.
For example, consider an algorithm that traverses through an array to find a specific element:
bool findElement(int arr[], int n, int key){ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (arr[i] == key) { return true; } } return false;}
2. Logarithmic Time Complexity: Big O(log n) Complexity
Logarithmic time complexity means that the running time of an algorithm is proportional to the logarithm of the input size.
For example, a binary search algorithm has a logarithmic time complexity:
int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int x){ if (r >= l) { int mid = l + (r - l) / 2; if (arr[mid] == x) return mid; if (arr[mid] > x) return binarySearch(arr, l, mid - 1, x); return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x); } return -1;}
3. Quadratic Time Complexity: Big O(n2) Complexity
Quadratic time complexity means that the running time of an algorithm is proportional to the square of the input size.
For example, a simple bubble sort algorithm has a quadratic time complexity:
void bubbleSort(int arr[], int n){ for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++) { if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) { swap(&arr[j], &arr[j + 1]); } } }}
4. Cubic Time Complexity: Big O(n3) Complexity
Cubic time complexity means that the running time of an algorithm is proportional to the cube of the input size.
For example, a naive matrix multiplication algorithm has a cubic time complexity:
void multiply(int mat1[][N], int mat2[][N], int res[][N]){ for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) { res[i][j] = 0; for (int k = 0; k < N; k++) res[i][j] += mat1[i][k] * mat2[k][j]; } }}
5. Polynomial Time Complexity: Big O(nk) Complexity
Polynomial time complexity refers to the time complexity of an algorithm that can be expressed as a polynomial function of the input size n. In Big O notation, an algorithm is said to have polynomial time complexity if its time complexity is O(nk), where k is a constant and represents the degree of the polynomial.
Algorithms with polynomial time complexity are generally considered efficient, as the running time grows at a reasonable rate as the input size increases. Common examples of algorithms with polynomial time complexity include linear time complexity O(n), quadratic time complexity O(n2), and cubic time complexity O(n3).
6. Exponential Time Complexity: Big O(2n) Complexity
Exponential time complexity means that the running time of an algorithm doubles with each addition to the input data set.
For example, the problem of generating all subsets of a set is of exponential time complexity:
void generateSubsets(int arr[], int n){ for (int i = 0; i < (1 << n); i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { if (i & (1 << j)) { cout << arr[j] << " "; } } cout << endl; }}
Factorial Time Complexity: Big O(n!) Complexity
Factorial time complexity means that the running time of an algorithm grows factorially with the size of the input. This is often seen in algorithms that generate all permutations of a set of data.
Here’s an example of a factorial time complexity algorithm, which generates all permutations of an array:
void permute(int* a, int l, int r){ if (l == r) { for (int i = 0; i <= r; i++) { cout << a[i] << " "; } cout << endl; } else { for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) { swap(a[l], a[i]); permute(a, l + 1, r); swap(a[l], a[i]); // backtrack } }}
If we plot the most common Big O notation examples, we would have graph like this:

How to Determine Big O Notation?
Big O notation is a mathematical notation used to describe the asymptotic behavior of a function as its input grows infinitely large. It provides a way to characterize the efficiency of algorithms and data structures.
Steps to Determine Big O Notation:
1. Identify the Dominant Term:
- Examine the function and identify the term with the highest order of growth as the input size increases.
- Ignore any constant factors or lower-order terms.
2. Determine the Order of Growth:
- The order of growth of the dominant term determines the Big O notation.
3. Write the Big O Notation:
- The Big O notation is written as O(f(n)), where f(n) represents the dominant term.
- For example, if the dominant term is n^2, the Big O notation would be O(n^2).
4. Simplify the Notation (Optional):
- In some cases, the Big O notation can be simplified by removing constant factors or by using a more concise notation.
- For instance, O(2n) can be simplified to O(n).
Example:
Function: f(n) = 3n3 + 2n2 + 5n + 1
- Dominant Term: 3n3
- Order of Growth: Cubic (n3)
- Big O Notation: O(n3)
- Simplified Notation: O(n3)
Mathematical Examples of Runtime Analysis:
Below table illustrates the runtime analysis of different orders of algorithms as the input size (n) increases.
| n | log(n) | n | n * log(n) | n^2 | 2^n | n! |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 1 | 10 | 10 | 100 | 1024 | 3628800 |
| 20 | 2.996 | 20 | 59.9 | 400 | 1048576 | 2.432902e+1818 |
Algorithmic Examples of Runtime Analysis:
Below table categorizes algorithms based on their runtime complexity and provides examples for each type.
| Type | Notation | Example Algorithms |
|---|---|---|
| Logarithmic | O(log n) | Binary Search |
| Linear | O(n) | Linear Search |
| Superlinear | O(n log n) | Heap Sort, Merge Sort |
| Polynomial | O(n^c) | Strassen’s Matrix Multiplication, Bubble Sort, Selection Sort, Insertion Sort, Bucket Sort |
| Exponential | O(c^n) | Tower of Hanoi |
| Factorial | O(n!) | Determinant Expansion by Minors, Brute force Search algorithm for Traveling Salesman Problem |
Algorithm Classes with Number of Operations and Execution Time:
Below are the classes of algorithms and their execution times on a computer executing 1 million operation per second (1 sec = 106 μsec = 103 msec):
Big O Notation Classes | f(n) | Big O Analysis (number of operations) for n = 10 | Execution Time (1 instruction/μsec) |
|---|---|---|---|
constant | O(1) | 1 | 1 μsec |
logarithmic | O(logn) | 3.32 | 3 μsec |
linear | O(n) | 10 | 10 μsec |
O(nlogn) | O(nlogn) | 33.2 | 33 μsec |
quadratic | O(n2) | 102 | 100 μsec |
cubic | O(n3) | 103 | 1msec |
exponential | O(2n) | 1024 | 10 msec |
factorial | O(n!) | 10! | 3.6288 sec |
Comparison of Big O Notation, Big Ω (Omega) Notation, and Big θ (Theta) Notation:
Below is a table comparing Big O notation, Ω (Omega) notation, and θ (Theta) notation:
| Notation | Definition | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Big O (O) | f(n) ≤ C * g(n) for all n ≥ n0 | Describes the upper bound of the algorithm’s running time in the worst case. |
| Ω (Omega) | f(n) ≥ C * g(n) for all n ≥ n0 | Describes the lower bound of the algorithm’s running time in the best case. |
| θ (Theta) | C1 * g(n) ≤ f(n) ≤ C2 * g(n) for n ≥ n0 | Describes both the upper and lower bounds of the algorithm’s running time. |
In each notation:
- f(n) represents the function being analyzed, typically the algorithm’s time complexity.
- g(n) represents a specific function that bounds f(n).
- C, C1, and C2 are constants.
- n0 is the minimum input size beyond which the inequality holds.
These notations are used to analyze algorithms based on their worst-case (Big O), best-case (Ω), and average-case (θ) scenarios.
Frequently Asked Questions about Big O Notation:
Question 1. What is Big O Notation?
Answer: Big O Notation is a mathematical notation used to describe the upper bound of an algorithm’s time complexity in terms of how it grows relative to the size of the input.
Question 2. Why is Big O Notation important?
Answer: It helps us analyze and compare the efficiency of algorithms by focusing on the worst-case scenario and understanding how their performance scales with input size.
Question 3. How is Big O Notation calculated?
Answer: Big O Notation is determined by identifying the dominant operation in an algorithm and expressing its time complexity in terms of n, where n represents the input size.
Question 4. What does O(1) mean in Big O Notation?
Answer: O(1) signifies constant time complexity, indicating that an algorithm’s execution time does not change regardless of the input size.
Question 5. What is the significance of different Big O complexities like O(log n) or O(n^2)?
Answer: Different complexities like O(log n) or O(n^2) represent how an algorithm’s performance scales as the input size increases, providing insights into its efficiency and scalability.
Question 6. Can Big O Notation be applied to space complexity as well?
Answer: Yes, Big O Notation can also be used to analyze and describe an algorithm’s space complexity, indicating how much memory it requires relative to the input size.
Related Article:
- Examples of Big-O analysis
- Design and Analysis of Algorithms
- Types of Asymptotic Notations in Complexity Analysis of Algorithms
- Analysis of Algorithms | Big – Ω (Big- Omega) Notation
- Analysis of Algorithms | little o and little omega notations
SoumyadeepDebnath
Improve
Previous Article
Introduction to Amortized Analysis
Next Article
Difference between Big O vs Big Theta Θ vs Big Omega Ω Notations